霍夫曼树的构造是使用了变长编码来减少数据所占空间,一般我们只考虑前缀码,即没有任何码字是其它码字的前缀。
我们的构造过程如下所示:
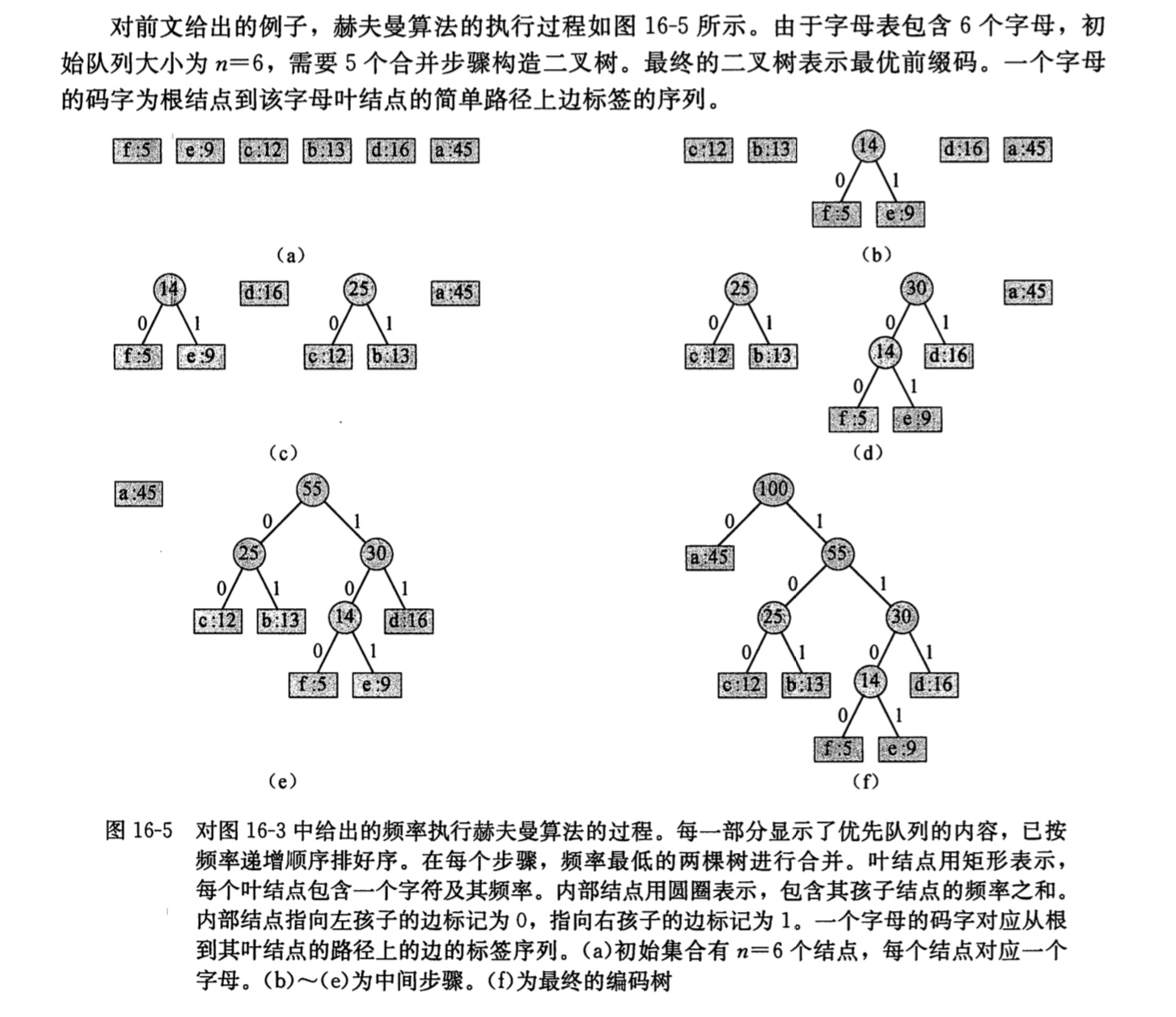
这里我们根据上述表示,我们每次总是“贪心”的选择两个最小的值来求和,并插入队列中。所以我们可以构造一个最小优先队列来存储各字母的频率。算法代码如下:
//
// main.cpp
// HUFFMAN
//
// Created by LZH on 2017/11/4.
// Copyright © 2017年 LZH. All rights reserved.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BitNode
{
int frep;
struct BitNode *left;
struct BitNode *right;
}Node;
//定义比较结构
struct cmp1{
bool operator ()(int &a,int &b){
return a>b;//最小值优先
}
};
//构造霍夫曼树
void HUFFMAN(int c, priority_queue<int, vector<int>, cmp1> &que1)
{
int n = c;
for (int i=0; i<n-1; i++) {
Node *newNodeZ = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *newNodeX = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *newNodeY = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNodeX->frep = que1.top();
que1.pop();
newNodeY->frep = que1.top();
que1.pop();
newNodeZ->left = newNodeX;
newNodeZ->right = newNodeY;
newNodeZ->frep =newNodeX->frep + newNodeY->frep;
que1.push(newNodeZ->frep);
}
}
int main() {
// priority_queue<int> que; //构造优先队列
int b[6] = {9,5,12,13,16,45};
// vector<int> a(b,b+6);
priority_queue<int , vector<int>, cmp1 >que1; //最小优先队列
for (int i=0; i<6; i++) {
que1.push(b[i]);
}
HUFFMAN(6, que1);
while (!que1.empty()) {
cout<<que1.top()<<' ';
que1.pop();
}
return 0;
}
最后输出为100,返回了编码树的根节点。