Linked List Cycle II
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
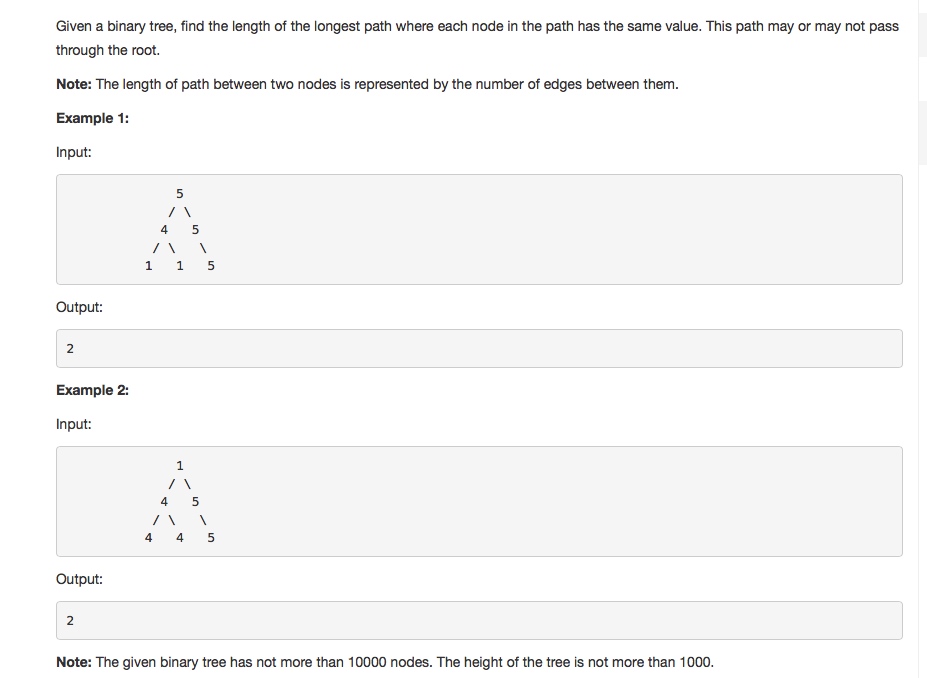
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head==NULL||head->next==NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ListNode *slow = head;
ListNode *fast = head;
ListNode *entry = head;
while (fast->next&&fast->next->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast==slow) {
while (slow!=entry) {
slow = slow->next;
entry = entry->next;
}
return entry;;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
Copyright © 2017 Powered by LZH, Theme used GitHub CSS.